The latest disruption, blockchain, and with it, the rise of cryptocurrencies show the way to the next stage, by creating decentralized computer networks capable of holding value, contracts, agreements, transactions in an encrypted manner.
Avinash Mudaliar, Siddhartha Banerjee and Srinivesh Tanukula
The internet, when it rose to global consciousness and became an overwhelming harbinger of disruption across society, economies and industry, created enormous wealth and value in disrupting existing practices and building cheaper, more accurate and efficient systems. Its advent promised much in terms of decentralizing and democratizing access to information, value and services. It promised to remove barriers and middlemen, vastly reduce operational and logistical costs in so many ways. And it has, to an extent, that the average human being can’t not be exposed to the internet multiple times every waking (and sleeping) day.
The latest disruption, blockchain, and with it, the rise of cryptocurrencies show the way to the next stage, by creating decentralized computer networks capable of holding value, contracts, agreements, transactions in an encrypted manner. By truly decentralizing the network that creates this value, it removes a dependency on any one authority or institution to reduce, remove or change the value of any such holding. And the first initiative off the table with the rise of blockchain computing would be Bitcoin, a digital currency or cryptocurrency.
he creator of bitcoin is Satoshi Nakamoto. The name is a pseudonym — no one knows who she or he actually is. Besides being the creator, Nakamoto holds enough bitcoin to flood the market, crashing its value and rendering it worthless. In addition, the founder can also influence any debate on future directions of Bitcoin, thereby holding huge potential implication for the future of crytocurrencies as a whole.
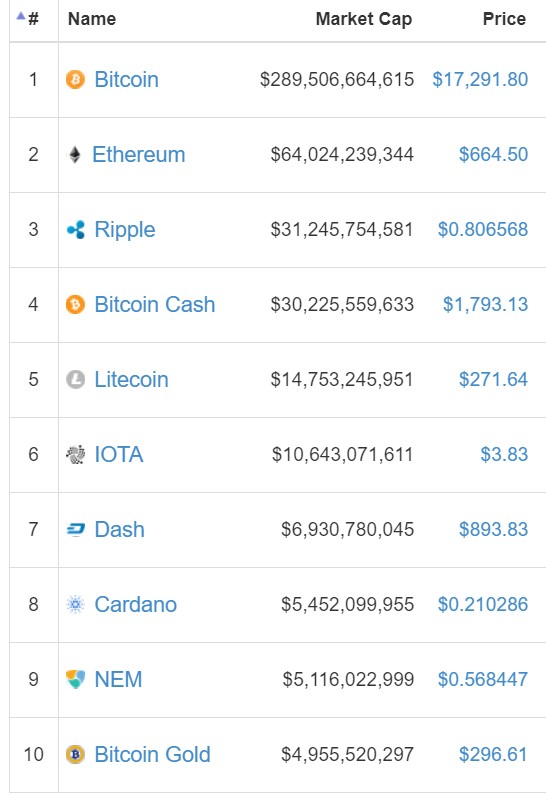
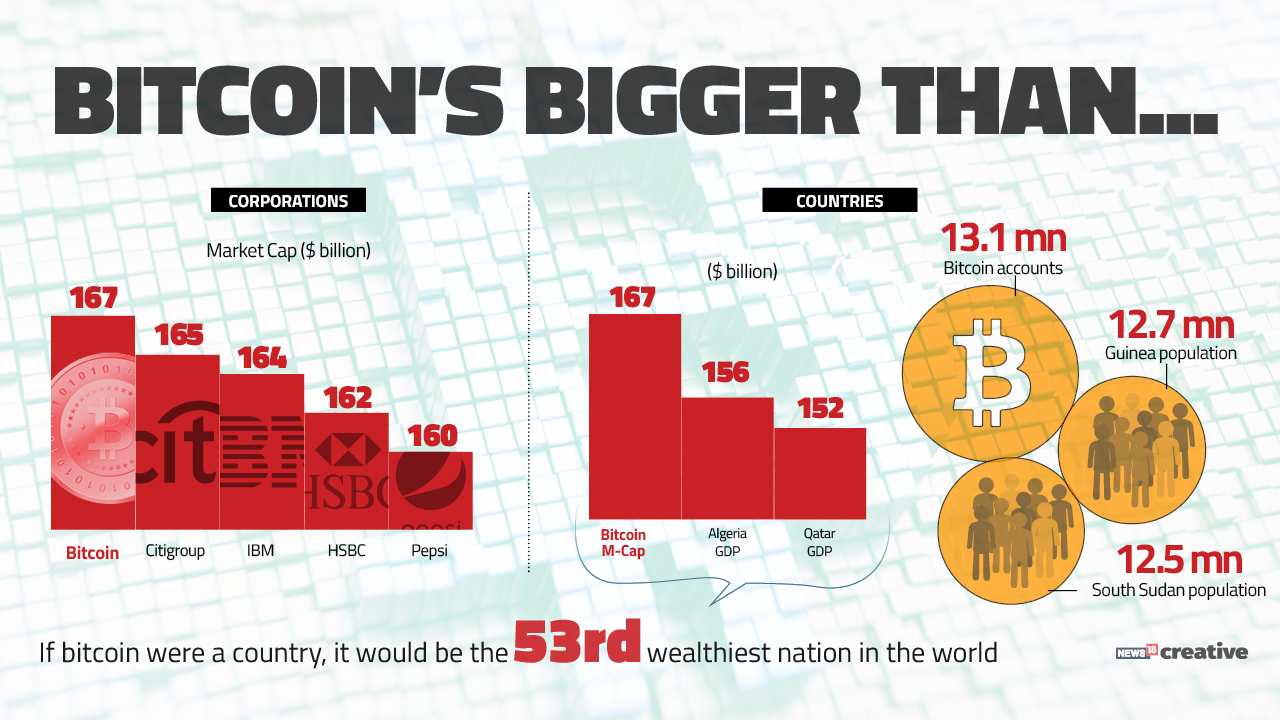
Bitcoin is but just one cryptocurrency. It is the leading one, however, with a total market value of USD 231 billion as of publishing time, accounting for 36% of the total value of all cryptocurrencies. The entire crypto currency market hit its peak value at about USD 700 billion in January 2018. Ethereum (13% market share) and Bitcoin cash (8%) are just two other major cryptocurrencies that are being traded today.
Satoshi Nakamoto: speculation on true identity
The mystery surrounding the identity of Bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto continues to cause intrigue. But nobody, not even his closest collaborators, has ever met Mr Nakamato in person. Although s/he not only wrote the white paper, but also the first version of the software powering the system, s/he eventually stopped participating. “I have moved on to other things,” s/he wrote in April 2011.
# In March 2014, a US magazine Newsweek, identified Dorian Satoshi Nakamoto, a man living in California, as the real Satoshi, but this turned out to be an embarrassing mistake. He lived near another possible suspect Hal Finney.
# Computer scientist Hal Finney, who was the recipient of the first Bitcoin transaction, is also sometime speculated to be the creator of Bitcoin. Finney was an early employee of cryptography company PGP and also knows “decentralised currency enthusiast” and scientist Nick Szabo who penned a paper on “bit gold” way back in 1998 and was said to be a fan of pseudonyms. Szabo seems to have asserted in 2011 that only he, Finney or Wei Dai – creator of Bitcoin precursor B-Money – could have been responsible for Bitcoin.
# Craig Wright, an Australian businessman and computer scientist, had in May 2016 posted online what he claimed to be proof that he is Satoshi Nakamoto. That was supported by Gavin Andresen, Mr Nakamoto’s successor as the lead developer of the bitcoin software; however, the claim was widely seem to have been debunked as fake.
# In November 2017, a blog post by former SpaceX employee claimed that Elon Musk was Satoshi Nakamoto, given his fondness for C++, known skill with cryptography, linguistic habits that seem close to Nakamoto’s and general all-round billionaire polymath-who-likes-to-solve-big-problems status; Musk himself has denied it.
Proof of Work
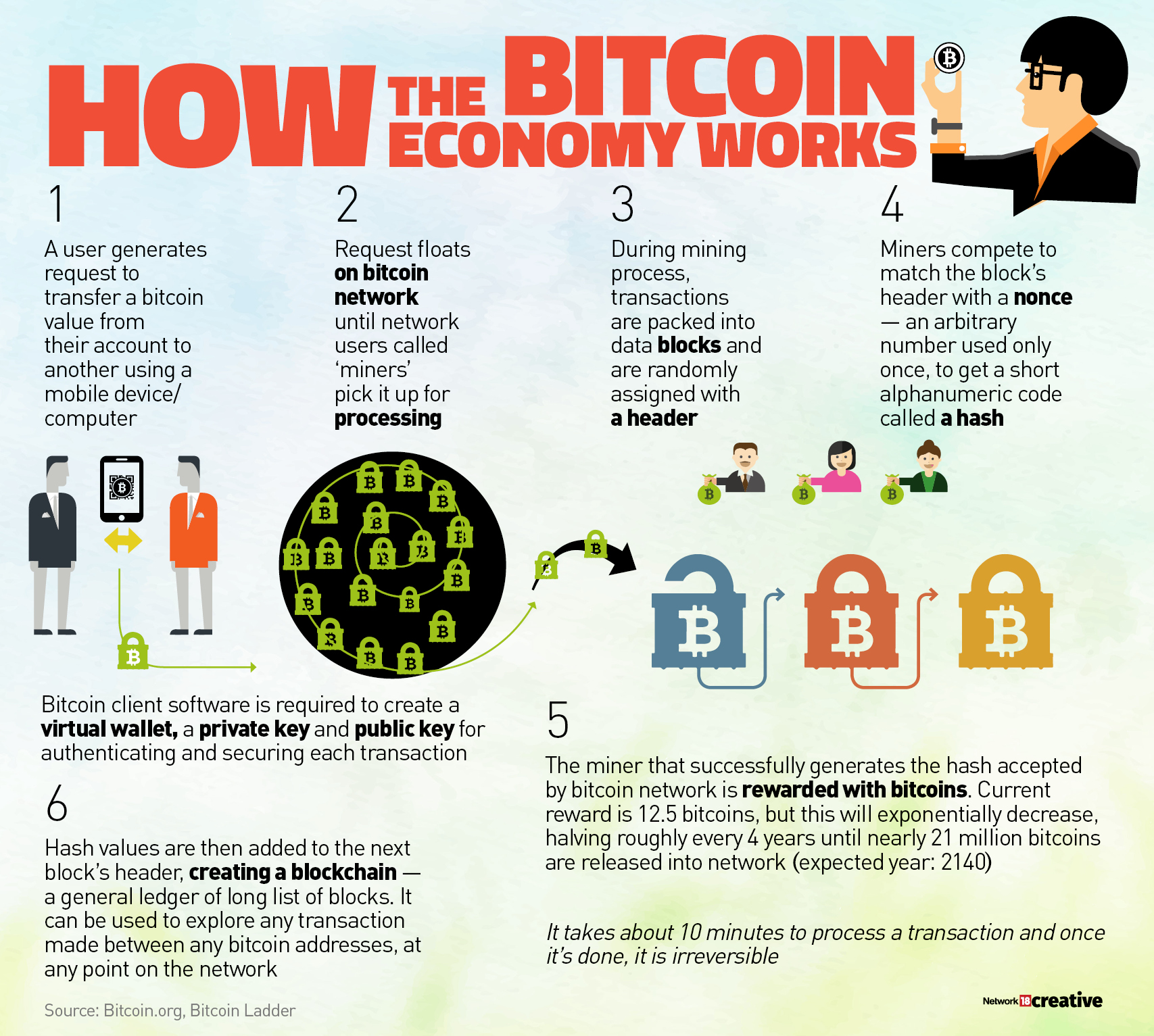
Proof of work is perhaps the strongest idea behind Nakamoto’s Bitcoin white paper because it allows trustless and distributed consensus. The Proof of work concept existed even before bitcoin, but Satoshi Nakamoto applied this technique to digital currency revolutionizing the way traditional transactions are set.
A trustless and distributed consensus system means that if you want to send and/or receive money from someone you don’t need to trust in third-party services. Proof of work is a requirement to define an expensive computer calculation, also called mining, that needs to be performed in order to create a new group of trustless transactions (the so-called block) on a distributed ledger called blockchain. All the network’s miners compete to be the first to find a solution for the mathematical problem that concerns the candidate block, a problem that cannot be solved in other ways than through brute force, essentially requiring a huge number of attempts. When a miner finally finds the right solution, he/she announces it to the whole network at the same time, receiving a cryptocurrency prize (the reward) provided by the protocol.
In this system the probability of mining a block is dependent on how much work is done by the miner. Originally published by Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor back in 1993 as an idea, the term “proof of work” was coined by Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels in a document published in 1999.
Bitcoin use